Recommended specialists
Article overview
There are different kinds of heart disease, some of which are congenital conditions, which people were born with. However, though the underlying mechanisms may vary, most of the common cardiovascular diseases and conditions develop over long periods of time, and their effects and symptoms become more noticeable later on in life.
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is a blockage of the coronary arteries, which prevents the heart muscles receiving an adequate supply of blood and oxygen. At its most serious, this can result in a sudden death with no warning, though the person concerned will typically have had some previous form of heart damage.
Ischemia
Ischemia is a type of coronary artery disease in which there is a reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. This shortage can be caused by a blockage or narrowing of the coronary arteries, but is often temporary and may result in minimal pain or symptoms. You may feel no discomfort while resting, though you may experience ischemia when you are stressed or when undergoing any form of physical exertion.
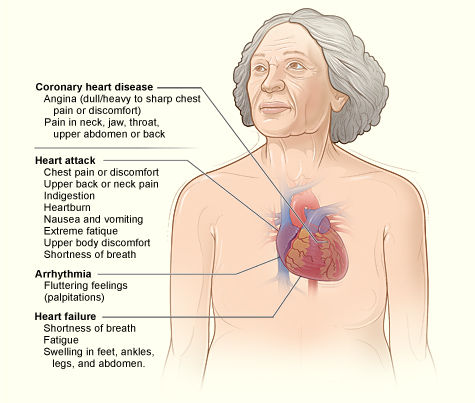
Angina
Angina is a type of pain or discomfort that occurs if your heart is not receiving sufficient oxygen and nutrients. These symptoms, which often feel like pressure or squeezing, can be the result of a narrowing of the arteries (atherosclerosis) or perhaps muscle spasms in the coronary arteries. Triggers for these spasms include cigarette smoke, strong emotions, cold environments and other sources. Though angina may cause pain, it will not typically cause any permanent damage. Symptoms usually occur when the heart works harder, but may also occur when you are relaxing. Classic angina begins in the chest region, before radiating down the left arm. It can also appear in the shoulders or in both arms, as well as the jaw, throat or neck regions.
Heart Attack
This occurs when a blockage stops blood flow to part of the heart muscle, which can suffer damage or die. If this is a temporary blockage, and blood, oxygen and nutrients are later restored, any damage may often be reversible. Thus, it is vitally important for any heart attack victim to receive urgent medical help. The typical symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort, which can extend to the shoulder, arm, back, neck or jaw. Other symptoms may include:
- feeling dizzy or faint
- nausea or vomiting
- excessive sweating
- a rapid heartbeat
- breathlessness
- extreme weakness
Heart Failure
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump sufficient blood for your body’s needs. It is not true that heart failure means the heart has stopped, or that a person may be about to die. This condition simply indicates that the heart is not functioning as well as it should; a situation that tends to develop gradually and gets worse over time. You should seek immediate medical advice if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- pulmonary congestion (a fluid build-up in the lungs)
- oedema (swelling of the feet, ankles or legs)
Other symptoms can include a cough, wheezing, sleep apnoea and fatigue.
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a malfunction of the heart’s electrical system, in which the heart beats irregularly, or else too fast or too slow. These abnormal rhythms can result in various symptoms, such as feeling weak, dizzy or faint, as well as breathlessness and heart palpitations, which may seem as if the heart is pounding or fluttering. Untreated, arrhythmia may be life threatening.
Heart Defects
Heart defects are primarily the result of an obstruction, which completely or partially prevents the normal flow of blood. This abnormal blockage or narrowing is known as a stenosis and can develop in your veins, arteries and heart valves.
Peripheral Arterial Disease
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a narrowing of those arteries that supply all parts of your body, other than your heart or brain. This narrowing is the result of a build-up of fatty materials (plaques) in your arteries, causing a decrease in the supply of oxygen-rich blood to regions such as your feet and legs. PAD symptoms may include:
- brown skin spots
- skin colour changes (e.g. pink legs turn blue)
- feeling cold
- hair loss on lower legs
- tingling and numbness
- cramp or pain following a short walk
- wounds heal slowly
- swelling
- ulcers